2026
|
 | Matt Gottsacker; Yahya Hmaiti; Mykola Maslych; Hiroshi Furuya; Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F. Welch; Joseph J. LaViola Jr. From One World to Another: Interfaces for Efficiently Transitioning Between Virtual Environments Proceedings Article Forthcoming In: ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '26), pp. 1-17, Forthcoming. @inproceedings{gottsacker2026worldswitch,
title = {From One World to Another: Interfaces for Efficiently Transitioning Between Virtual Environments},
author = {Matt Gottsacker and Yahya Hmaiti and Mykola Maslych and Hiroshi Furuya and Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F. Welch and Joseph J. LaViola Jr.},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/CHI2026___FullPaper__WorldSwitchUI-4.pdf},
doi = {10.1145/3772318.3791912},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-04-13},
urldate = {2026-04-13},
booktitle = {ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '26)},
pages = {1-17},
abstract = {Personal computers and handheld devices provide keyboard shortcuts and swipe gestures to enable users to efficiently switch between applications, whereas today's virtual reality (VR) systems do not. In this work, we present an exploratory study on user interface aspects to support efficient switching between worlds in VR. We created eight interfaces that afford previewing and selecting from the available virtual worlds, including methods using portals and worlds-in-miniature (WiMs). To evaluate these methods, we conducted a controlled within-subjects empirical experiment (N=22) where participants frequently transitioned between six different environments to complete an object collection task. Our quantitative and qualitative results show that WiMs supported rapid acquisition of high-level spatial information while searching and were deemed most efficient by participants while portals provided fast pre-orientation. Finally, we present insights into the applicability, usability, and effectiveness of the VR world switching methods we explored, and provide recommendations for their application and future context/world switching techniques and interfaces.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Personal computers and handheld devices provide keyboard shortcuts and swipe gestures to enable users to efficiently switch between applications, whereas today's virtual reality (VR) systems do not. In this work, we present an exploratory study on user interface aspects to support efficient switching between worlds in VR. We created eight interfaces that afford previewing and selecting from the available virtual worlds, including methods using portals and worlds-in-miniature (WiMs). To evaluate these methods, we conducted a controlled within-subjects empirical experiment (N=22) where participants frequently transitioned between six different environments to complete an object collection task. Our quantitative and qualitative results show that WiMs supported rapid acquisition of high-level spatial information while searching and were deemed most efficient by participants while portals provided fast pre-orientation. Finally, we present insights into the applicability, usability, and effectiveness of the VR world switching methods we explored, and provide recommendations for their application and future context/world switching techniques and interfaces. |
 | Hiroshi Furuya; Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman; Zubin Datta Choudhary; Matt Gottsacker; Ahinya Alwin; Lee Lisle; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F Welch Effects of Multisensory Feedback and Real-World Priming on Presence and Copresence in Mixed Reality Drone Simulation Proceedings Article Forthcoming In: Proceedings of the 2026 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (IEEE VRW): 2nd Annual Workshop on Real and Virtual Spaces Influences (ReVISI), pp. 1-7, Forthcoming. @inproceedings{furuya-real-world-priming-26,
title = {Effects of Multisensory Feedback and Real-World Priming on Presence and Copresence in Mixed Reality Drone Simulation},
author = {Hiroshi Furuya and Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman and Zubin Datta Choudhary and Matt Gottsacker and Ahinya Alwin and Lee Lisle and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/VR26_Revisi__Real_World_Priming_for_VR_Experiences-3.pdf},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-03-21},
urldate = {2026-03-21},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2026 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (IEEE VRW): 2nd Annual Workshop on Real and Virtual Spaces Influences (ReVISI)},
pages = {1-7},
abstract = {Virtual reality (VR) experiences often rely on multisensory cues and realistic interactions to support convincing interpretations of virtual events and agents. This study examines how two factors, real-world priming and multisensory feedback, shape users’ perceptions of a virtual drone in a mixed-reality simulation. We conducted a mixed-design experiment where participants experienced either a physical drone flyover or no physical drone encounter, followed by audiovisual and multisensory drone flyovers in VR. Multisensory feedback increased co-presence and perceived realism specifically for participants who had encountered the real drone. In contrast, neither manipulation significantly affected standard presence measures. These findings highlight distinctions among presence-related constructs and suggest that recent real-world experiences can make certain multisensory cues be perceived as more realistic, even when they do not increase presence itself.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Virtual reality (VR) experiences often rely on multisensory cues and realistic interactions to support convincing interpretations of virtual events and agents. This study examines how two factors, real-world priming and multisensory feedback, shape users’ perceptions of a virtual drone in a mixed-reality simulation. We conducted a mixed-design experiment where participants experienced either a physical drone flyover or no physical drone encounter, followed by audiovisual and multisensory drone flyovers in VR. Multisensory feedback increased co-presence and perceived realism specifically for participants who had encountered the real drone. In contrast, neither manipulation significantly affected standard presence measures. These findings highlight distinctions among presence-related constructs and suggest that recent real-world experiences can make certain multisensory cues be perceived as more realistic, even when they do not increase presence itself. |
![[Poster] Can You See It? Evaluating Color Visibility in Simulated Outdoor Environments](https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/teaser_AA-150x150.png) | Ahinya Alwin; Matthew Gottsacker; Hiroshi Furuya; Armin Delmo; Lee Lisle; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F. Welch [Poster] Can You See It? Evaluating Color Visibility in Simulated Outdoor Environments Proceedings Article Forthcoming In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR) 2026., Forthcoming. @inproceedings{Alwin2026_2,
title = {[Poster] Can You See It? Evaluating Color Visibility in Simulated Outdoor Environments},
author = {Ahinya Alwin and Matthew Gottsacker and Hiroshi Furuya and Armin Delmo and Lee Lisle and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F. Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/vr26b-sub1299-cam-i5.pdf},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-03-21},
urldate = {2026-03-21},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR) 2026.},
journal = {Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR) 2026, Daegu, South Korea.},
abstract = {Evaluating color visibility in outdoor augmented reality (AR) is challenging due to the visual complexity and variability of real world environments. Outdoor scenes feature diverse textures and lighting conditions, limiting the applicability of visibility evaluation methods developed for simple or static backgrounds. This work introduces a methodology for evaluating AR cue color visibility in an outdoor environment by sampling visibility across realistic scenes and identifying design considerations for evaluating color visibility under dynamic, visually complex conditions},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Evaluating color visibility in outdoor augmented reality (AR) is challenging due to the visual complexity and variability of real world environments. Outdoor scenes feature diverse textures and lighting conditions, limiting the applicability of visibility evaluation methods developed for simple or static backgrounds. This work introduces a methodology for evaluating AR cue color visibility in an outdoor environment by sampling visibility across realistic scenes and identifying design considerations for evaluating color visibility under dynamic, visually complex conditions |
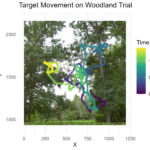 | Ahinya Alwin; Matthew Gottsacker; Hiroshi Furuya; Lee Lisle; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F. Welch Moving Towards Visibility Evaluation in Augmented Reality Using Simulated Environments and Continuous Psychophysics Proceedings Article Forthcoming In: Proceedings of the 2026 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (IEEE VRW): Third International Workshop on Perception-driven Graphics and Displays for VR and AR (PerGraVAR), Forthcoming. @inproceedings{Alwin2026b,
title = {Moving Towards Visibility Evaluation in Augmented Reality Using Simulated Environments and Continuous Psychophysics},
author = {Ahinya Alwin and Matthew Gottsacker and Hiroshi Furuya and Lee Lisle and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F. Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/ieee_vr_2026_workshops_pergravar__visibility_evaluation_in_augmented_reality_using_simulated_environments_and_continuous_psychophysics_013026/},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-03-21},
urldate = {2026-03-21},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2026 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (IEEE VRW): Third International Workshop on Perception-driven Graphics and Displays for VR and AR (PerGraVAR)},
abstract = {Assessing the visibility of augmented reality (AR) cues in outdoor environments is challenging due to complex background structure, motion, and lighting variability. Simulating AR cues within virtual reality (VR) enables controlled manipulation and measurement of these factors while preserving immersive viewing conditions. This work presents a perception-driven methodology for evaluating AR cue visibility that combines simulated AR cues in VR, high resolution stereoscopic 360◦ video, and continuous psychophysics. Using this methodology, tracking-based performance data provide a continuous behavioral measure of visibility in complex scenes. Multiple analysis approaches are examined to support interpretation of tracking-based measures of perceptual performance in visually complex scenes. Together, this work illustrates progress toward a more ecologically valid and objective framework for studying AR cue visibility in outdoor settings.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Assessing the visibility of augmented reality (AR) cues in outdoor environments is challenging due to complex background structure, motion, and lighting variability. Simulating AR cues within virtual reality (VR) enables controlled manipulation and measurement of these factors while preserving immersive viewing conditions. This work presents a perception-driven methodology for evaluating AR cue visibility that combines simulated AR cues in VR, high resolution stereoscopic 360◦ video, and continuous psychophysics. Using this methodology, tracking-based performance data provide a continuous behavioral measure of visibility in complex scenes. Multiple analysis approaches are examined to support interpretation of tracking-based measures of perceptual performance in visually complex scenes. Together, this work illustrates progress toward a more ecologically valid and objective framework for studying AR cue visibility in outdoor settings. |
 | Zubin Datta Choudhary; Ferran Argelaguet; Gerd Bruder; and Gregory F. Welch Teleportation Destination Previews Support Memory Retention During Virtual Navigation Proceedings Article Forthcoming In: Proceedings of the 2026 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR); Daegu, South Korea, March 21-25, Forthcoming. @inproceedings{Choudhary2026,
title = {Teleportation Destination Previews Support Memory Retention During Virtual Navigation},
author = {Zubin Datta Choudhary and Ferran Argelaguet and Gerd Bruder and and Gregory F. Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/previews-effecting-memory/},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-03-21},
urldate = {2026-03-21},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2026 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR); Daegu, South Korea, March 21-25},
abstract = {Teleportation is one of the most widely used locomotion techniques in virtual reality (VR) because it is efficient, minimizes motion sickness, and enables large-scale spatial traversal with minimal effort. However, research on the Doorway Effect shows that spatial transitions can impair memory of information encountered just before the transition. Event Segmentation Theory (EST) explains this by proposing that salient changes disrupt a person’s working memory representation, causing recently encoded information to be replaced and reducing its availability for retrieval. By extension, the design of spatial transitions in VR may influence whether memory is disrupted or preserved, which could be a consideration in applied contexts such as education and training. One way to mitigate such impairment is to provide predictive cues about the upcoming change to reduce disruption. In VR, this can be implemented through teleportation previews, which give users a glimpse of the destination before arrival. In this experiment, we adapted the Doorway Effect paradigm to examine how two teleportation design factors — preview availability and environmental change — affect memory. Using a within-subjects 2 × 2 design (N = 27), participants studied a set of 3D objects, then teleported either within the same environment or into a different one, with or without a preview of the destination. After each transition, they completed a visual recognition task. Results showed two key findings: (1) without previews, recognition declined when teleporting into a different environment compared to remaining in the same one, and (2) when transitioning between different environments, providing a preview improved recognition relative to no preview. Together, these results indicate that both the distinctiveness of environments and the availability of previews shape memory during VR transitions. We discuss how these findings align with EST, highlight the cognitive consequences of teleportation design, and provide guidance for designing transitions that better support memory in applied contexts such as education and training.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {forthcoming},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Teleportation is one of the most widely used locomotion techniques in virtual reality (VR) because it is efficient, minimizes motion sickness, and enables large-scale spatial traversal with minimal effort. However, research on the Doorway Effect shows that spatial transitions can impair memory of information encountered just before the transition. Event Segmentation Theory (EST) explains this by proposing that salient changes disrupt a person’s working memory representation, causing recently encoded information to be replaced and reducing its availability for retrieval. By extension, the design of spatial transitions in VR may influence whether memory is disrupted or preserved, which could be a consideration in applied contexts such as education and training. One way to mitigate such impairment is to provide predictive cues about the upcoming change to reduce disruption. In VR, this can be implemented through teleportation previews, which give users a glimpse of the destination before arrival. In this experiment, we adapted the Doorway Effect paradigm to examine how two teleportation design factors — preview availability and environmental change — affect memory. Using a within-subjects 2 × 2 design (N = 27), participants studied a set of 3D objects, then teleported either within the same environment or into a different one, with or without a preview of the destination. After each transition, they completed a visual recognition task. Results showed two key findings: (1) without previews, recognition declined when teleporting into a different environment compared to remaining in the same one, and (2) when transitioning between different environments, providing a preview improved recognition relative to no preview. Together, these results indicate that both the distinctiveness of environments and the availability of previews shape memory during VR transitions. We discuss how these findings align with EST, highlight the cognitive consequences of teleportation design, and provide guidance for designing transitions that better support memory in applied contexts such as education and training. |
2025
|
 | Taylor Laird; Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman; Gerd Bruder; Carolina Cruz-Neira; Dirk Reiners You Have Arrive... Kind Of: Investigating the Limits of Undetectable Destination Displacement During Teleportation Proceedings Article In: Proceedings of the 2025 31st ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology, pp. 1–11, 2025. @inproceedings{lairddeguzman2025you,
title = {You Have Arrive... Kind Of: Investigating the Limits of Undetectable Destination Displacement During Teleportation},
author = {Taylor Laird and Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman and Gerd Bruder and Carolina Cruz-Neira and Dirk Reiners},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/VRST_2025__You_Have_Arrived____Kind_of__Investigating_the_Limits_of_Undetectable_Destination_Displacement_During_Teleportation_FINAL.pdf},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3756884.3766040},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-12},
urldate = {2025-11-12},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2025 31st ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology},
pages = {1--11},
abstract = {Teleportation has become a popular locomotion method for virtual reality due to lesser demands on physical space and decreased levels of motion sickness compared to other methods. However, prior work has shown that these advantages come at the cost of impaired spatial perception and awareness, the extent to which is still largely unknown. In this work, we present a within-subjects study (N = 29) that explores the effects of teleportation on spatial perception by investigating how much humans can be unknowingly displaced relative to their intended destination during teleportation. After teleporting to the specified location, participants indicated the direction and magnitude (small, medium, large) of the perceived shift or rotation. Displacement from the target happened either as a translation in the forward- or strafe-axis, or a rotation about the up-axis at the intended target. Each displacement condition included eleven offsets that were repeated six times. Our results indicate points of subjective equality, which show a significant perceptual shift along the forward-direction, as well as detection thresholds, which indicate a comparatively wide range in which humans are unable to detect induced shifts. Furthermore, our results show that even if humans are able to detect these shifts, larger ones can be introduced before their magnitudes are rated as medium or large, which provides ample opportunities for interface designers who want to leverage these results in virtual reality.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Teleportation has become a popular locomotion method for virtual reality due to lesser demands on physical space and decreased levels of motion sickness compared to other methods. However, prior work has shown that these advantages come at the cost of impaired spatial perception and awareness, the extent to which is still largely unknown. In this work, we present a within-subjects study (N = 29) that explores the effects of teleportation on spatial perception by investigating how much humans can be unknowingly displaced relative to their intended destination during teleportation. After teleporting to the specified location, participants indicated the direction and magnitude (small, medium, large) of the perceived shift or rotation. Displacement from the target happened either as a translation in the forward- or strafe-axis, or a rotation about the up-axis at the intended target. Each displacement condition included eleven offsets that were repeated six times. Our results indicate points of subjective equality, which show a significant perceptual shift along the forward-direction, as well as detection thresholds, which indicate a comparatively wide range in which humans are unable to detect induced shifts. Furthermore, our results show that even if humans are able to detect these shifts, larger ones can be introduced before their magnitudes are rated as medium or large, which provides ample opportunities for interface designers who want to leverage these results in virtual reality. |
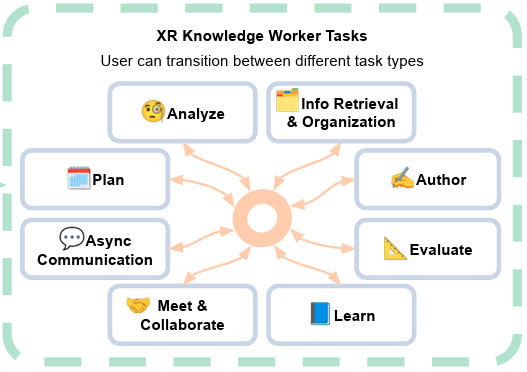 | Matt Gottsacker; Yahya Hmaiti; Mykola Maslych; Hiroshi Furuya; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F Welch; Joseph J. LaViola Jr. XR-First Design for Productivity: A Conceptual Framework for Enabling Efficient Task Switching in XR Proceedings Article In: IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR) Adjunct Proceedings, 2025. @inproceedings{nokey,
title = {XR-First Design for Productivity: A Conceptual Framework for Enabling Efficient Task Switching in XR},
author = {Matt Gottsacker and Yahya Hmaiti and Mykola Maslych and Hiroshi Furuya and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F Welch and Joseph J. LaViola Jr.},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/ISMAR25__Workshop_Paper__xrWORKS__VR_World_Switch_UI-11.pdf},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-08},
urldate = {2025-10-08},
booktitle = {IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR) Adjunct Proceedings},
abstract = {A core component of completing tasks efficiently in computer supported knowledge work is the ability for users to rapidly switch their focus (and interaction) across different applications using various shortcuts and gestures. This feature set has been explored in research, and several modern consumer extended reality (XR) headsets now support loading multiple applications windows at once. However, many XR applications that are useful for knowledge work involve rich spatial information, which window-based metaphors do not sufficiently represent nor afford appropriate interaction. In modern XR headsets, such immersive applications run as siloed experiences, requiring the user to fully exit one before starting another. We present a vision for achieving an XR-first, user-centric paradigm for efficient context switching in XR to encourage and guide future research and development of XR context- and task-switching interfaces.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
A core component of completing tasks efficiently in computer supported knowledge work is the ability for users to rapidly switch their focus (and interaction) across different applications using various shortcuts and gestures. This feature set has been explored in research, and several modern consumer extended reality (XR) headsets now support loading multiple applications windows at once. However, many XR applications that are useful for knowledge work involve rich spatial information, which window-based metaphors do not sufficiently represent nor afford appropriate interaction. In modern XR headsets, such immersive applications run as siloed experiences, requiring the user to fully exit one before starting another. We present a vision for achieving an XR-first, user-centric paradigm for efficient context switching in XR to encourage and guide future research and development of XR context- and task-switching interfaces. |
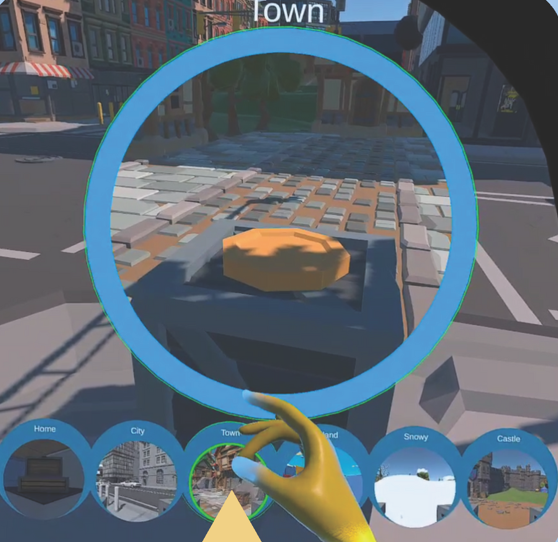 | Matt Gottsacker; Yahya Hmaiti; Mykola Maslych; Hiroshi Furuya; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F Welch; Joseph J. LaViola Jr. From Alt-Tab to World-Snap: Exploring Different Metaphors for Swift and Seamless VR World Switching Proceedings Article In: IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality, pp. 1-2, 2025. @inproceedings{nokey,
title = {From Alt-Tab to World-Snap: Exploring Different Metaphors for Swift and Seamless VR World Switching},
author = {Matt Gottsacker and Yahya Hmaiti and Mykola Maslych and Hiroshi Furuya and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F Welch and Joseph J. LaViola Jr.},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/ISMAR25__Demo__VR_World_Switch_UI.pdf},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-10-08},
urldate = {2025-10-08},
booktitle = {IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality},
pages = {1-2},
abstract = {Today's personal computers and handheld devices afford users the ability to rapidly switch between different applications, e.g., using keyboard shortcuts and swipe gestures. In today's virtual reality (VR) systems, immersive applications are siloed experiences that users must fully exit before starting another. We demonstrate eight prototypes of world switching interfaces that let users preview, select, and transition across multiple virtual environments in a continuous interaction, mirroring the ``Alt+Tab" agility of desktop multitasking. We developed these techniques based on portals and worlds-in-miniature (WiM) metaphors that reveal the destination environment before triggering a full transition. },
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Today's personal computers and handheld devices afford users the ability to rapidly switch between different applications, e.g., using keyboard shortcuts and swipe gestures. In today's virtual reality (VR) systems, immersive applications are siloed experiences that users must fully exit before starting another. We demonstrate eight prototypes of world switching interfaces that let users preview, select, and transition across multiple virtual environments in a continuous interaction, mirroring the ``Alt+Tab" agility of desktop multitasking. We developed these techniques based on portals and worlds-in-miniature (WiM) metaphors that reveal the destination environment before triggering a full transition. |
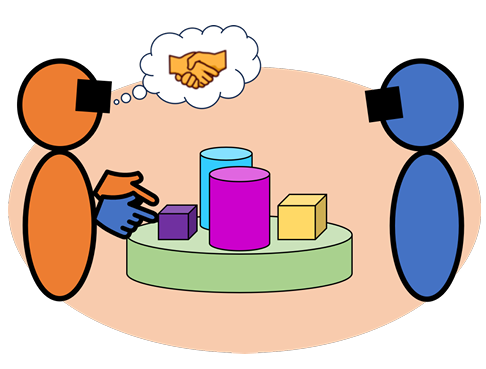 | Matt Gottsacker; Nels Numan; Anthony Steed; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F. Welch; Steve Feiner Decoupled Hands: An Approach for Aligning Perspectives in Collaborative Mixed Reality Proceedings Article In: ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '25), 2025. @inproceedings{gottsacker2025perspectives,
title = {Decoupled Hands: An Approach for Aligning Perspectives in Collaborative Mixed Reality},
author = {Matt Gottsacker and Nels Numan and Anthony Steed and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F. Welch and Steve Feiner},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/CHI25__LBW__MR_Perspective_Alignment_preprint.pdf},
doi = {10.1145/3706599.3720219},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-04-26},
urldate = {2025-04-26},
booktitle = {ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '25)},
abstract = {When collaborating relative to a shared 3D virtual object in mixed reality (MR), users may experience communication issues arising from differences in perspective. These issues include occlusion (e.g., one user not being able to see what the other is referring to) and inefficient spatial references (e.g., "to the left of this" may be confusing when users are positioned opposite to each other). This paper presents a novel technique for automatic perspective alignment in collaborative MR involving co-located interaction centered around a shared virtual object. To align one user’s perspective on the object with a collaborator’s, a local copy of the object and any other virtual elements that reference it (e.g., the collaborator’s hands) are dynamically transformed. The technique does not require virtual travel and preserves face-to-face interaction. We created a prototype application to demonstrate our technique and present an evaluation methodology for related MR collaboration and perspective alignment scenarios.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
When collaborating relative to a shared 3D virtual object in mixed reality (MR), users may experience communication issues arising from differences in perspective. These issues include occlusion (e.g., one user not being able to see what the other is referring to) and inefficient spatial references (e.g., "to the left of this" may be confusing when users are positioned opposite to each other). This paper presents a novel technique for automatic perspective alignment in collaborative MR involving co-located interaction centered around a shared virtual object. To align one user’s perspective on the object with a collaborator’s, a local copy of the object and any other virtual elements that reference it (e.g., the collaborator’s hands) are dynamically transformed. The technique does not require virtual travel and preserves face-to-face interaction. We created a prototype application to demonstrate our technique and present an evaluation methodology for related MR collaboration and perspective alignment scenarios. |
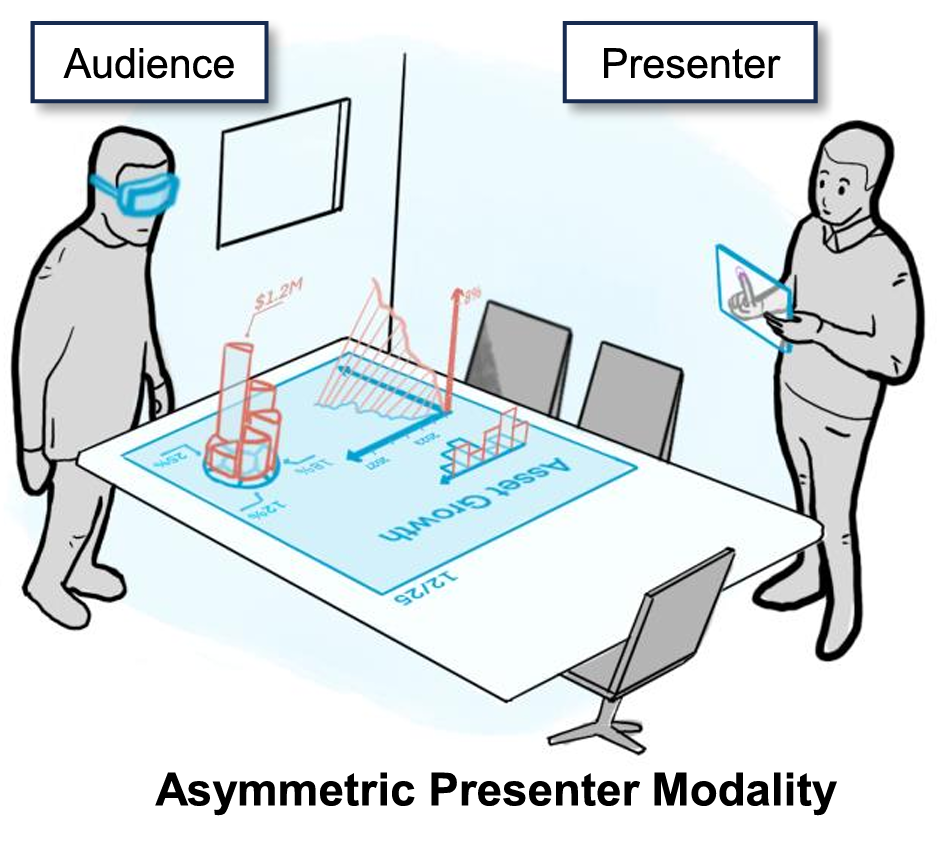 | Matt Gottsacker; Mengyu Chen; David Saffo; Feiyu Lu; Benjamin Lee; Blair MacIntyre Examining the Effects of Immersive and Non-Immersive Presenter Modalities on Engagement and Social Interaction in Co-located Augmented Presentations Proceedings Article In: ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '25), 2025. @inproceedings{gottsacker2025presentations,
title = {Examining the Effects of Immersive and Non-Immersive Presenter Modalities on Engagement and Social Interaction in Co-located Augmented Presentations},
author = {Matt Gottsacker and Mengyu Chen and David Saffo and Feiyu Lu and Benjamin Lee and Blair MacIntyre},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/CHI25__Paper__Immersive_Presentation_Study_preprint.pdf},
doi = {10.1145/3706598.3713346},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-04-26},
urldate = {2025-04-26},
booktitle = {ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI '25)},
abstract = {Head-worn augmented reality (AR) allows audiences to be immersed and engaged in stories told by live presenters. While presenters may also be in AR to have the same level of immersion and awareness as their audience, this symmetric presentation style may diminish important social cues such as eye contact. In this work, we examine the effects this (a)symmetry has on engagement, group awareness, and social interaction in co-located one-on-one augmented presentations. We developed a presentation system incorporating 2D/3D content that audiences can view and interact with in AR, with presenters controlling and delivering the presentation in either a symmetric style in AR, or an asymmetric style with a handheld tablet. We conducted a within- and between-subjects evaluation with 12 participant pairs to examine the differences between these symmetric and asymmetric presentation modalities. From our findings, we extracted four themes and derived strategies and guidelines for designers interested in augmented presentations.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Head-worn augmented reality (AR) allows audiences to be immersed and engaged in stories told by live presenters. While presenters may also be in AR to have the same level of immersion and awareness as their audience, this symmetric presentation style may diminish important social cues such as eye contact. In this work, we examine the effects this (a)symmetry has on engagement, group awareness, and social interaction in co-located one-on-one augmented presentations. We developed a presentation system incorporating 2D/3D content that audiences can view and interact with in AR, with presenters controlling and delivering the presentation in either a symmetric style in AR, or an asymmetric style with a handheld tablet. We conducted a within- and between-subjects evaluation with 12 participant pairs to examine the differences between these symmetric and asymmetric presentation modalities. From our findings, we extracted four themes and derived strategies and guidelines for designers interested in augmented presentations. |
![[Poster] Inducing Unintentional Positional Drift (UPD) in Virtual Reality via Physical Rotations and the Illusion of Leaning](https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Roll-Example-e1741105590923-150x150.jpg) | Zubin Datta Choudhary; Ferran Argelaguet; Gerd Bruder; Greg Welch [Poster] Inducing Unintentional Positional Drift (UPD) in Virtual Reality via Physical Rotations and the Illusion of Leaning Proceedings Article In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR) 2025., 2025. @inproceedings{Choudhary2025,
title = {[Poster] Inducing Unintentional Positional Drift (UPD) in Virtual Reality via Physical Rotations and the Illusion of Leaning},
author = {Zubin Datta Choudhary and Ferran Argelaguet and Gerd Bruder and Greg Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Camera-Ready_UPD_Roll_Poster_IEEE_VR_25.pdf},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-03-10},
urldate = {2025-03-10},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR) 2025.},
abstract = {In Virtual Reality (VR) users often turn their bodies during experiences. Virtual navigation techniques use body rotations and virtual forward translations to simulate movement. Despite being designed for stationary use, these techniques can cause Unintentional Positional Drift (UPD), impacting user safety and VR experiences. We carried out a human-participant study, approved by our university ethics board, involving 20 participants performing repetitive rotation tasks. Our study focused on intentionally inducing UPD via physical rotations by adding an offset to the VR camera’s roll angle, creating a visual illusion of “leaning” or “banking.” Our results show that camera roll offsets induced UPD along participants initial left-right axis under specific conditions. Additionally, rotation magnitude and forward translation flow affected UPD, while no significant effects were found due to rotation direction.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
In Virtual Reality (VR) users often turn their bodies during experiences. Virtual navigation techniques use body rotations and virtual forward translations to simulate movement. Despite being designed for stationary use, these techniques can cause Unintentional Positional Drift (UPD), impacting user safety and VR experiences. We carried out a human-participant study, approved by our university ethics board, involving 20 participants performing repetitive rotation tasks. Our study focused on intentionally inducing UPD via physical rotations by adding an offset to the VR camera’s roll angle, creating a visual illusion of “leaning” or “banking.” Our results show that camera roll offsets induced UPD along participants initial left-right axis under specific conditions. Additionally, rotation magnitude and forward translation flow affected UPD, while no significant effects were found due to rotation direction. |
 | Hiroshi Furuya; Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman; Zubin Datta Choudhary; Matthew Gottsacker; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F. Welch How Does Presence Affect Trust in Simulated Autonomous Agents? Proceedings Article In: Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (IEEE VRW): 1st Annual Workshop on Real and Virtual Spaces Influences (ReVISI), pp. 1-2, 2025. @inproceedings{Furuya2025hc,
title = {How Does Presence Affect Trust in Simulated Autonomous Agents?},
author = {Hiroshi Furuya and Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman and Zubin Datta Choudhary and Matthew Gottsacker and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F. Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/How_Does_Presence_Affect_Trust_in_Simulated_Autonomous_Agents.pdf},
doi = {10.1109/VRW66409.2025.00109},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-03-08},
urldate = {2025-03-08},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces Abstracts and Workshops (IEEE VRW): 1st Annual Workshop on Real and Virtual Spaces Influences (ReVISI)},
pages = {1-2},
abstract = {Autonomous agents present important novel capabilities for a wide swath of applications like simulating interactions between humans and agents. Simulating these interactions in VR has become an important tool for evaluating the effects of agents on human behavior and performance, including human-agent trust. This position paper presents research opportunities in the use of real-world multi-modal feedback and real-world priming experiences may have on the validity of trust measurements taken from simulated human-agent interactions in VR. In addition, it presents a hypothetical experiment addressing research questions related to this topic.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Autonomous agents present important novel capabilities for a wide swath of applications like simulating interactions between humans and agents. Simulating these interactions in VR has become an important tool for evaluating the effects of agents on human behavior and performance, including human-agent trust. This position paper presents research opportunities in the use of real-world multi-modal feedback and real-world priming experiences may have on the validity of trust measurements taken from simulated human-agent interactions in VR. In addition, it presents a hypothetical experiment addressing research questions related to this topic. |
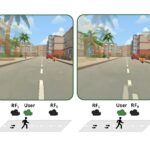 | Tongyu Nie; Courtney Hutton Pospick; Ville Cantory; Danhua Zhang; Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman; Victoria Interrante; Isayas Berhe Adhanom; Evan Suma Rosenberg Peripheral Teleportation: A Rest Frame Design to Mitigate Cybersickness During Virtual Locomotion Journal Article In: IEEE Transaction on Visualization and Computer Graphics, pp. 1-10, 2025, (Best Paper Award, IEEE VR 2025). @article{nie2025pt,
title = {Peripheral Teleportation: A Rest Frame Design to Mitigate Cybersickness During Virtual Locomotion},
author = {Tongyu Nie and Courtney Hutton Pospick and Ville Cantory and Danhua Zhang and Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman and Victoria Interrante and Isayas Berhe Adhanom and Evan Suma Rosenberg},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/2025_IEEE_VR__TVCG__Peripheral_Teleportation.pdf},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-02-25},
urldate = {2025-02-25},
journal = {IEEE Transaction on Visualization and Computer Graphics},
pages = {1-10},
abstract = {Mitigating cybersickness can improve the usability of virtual reality (VR) and increase its adoption. The most widely used technique, dynamic field-of-view (FOV) restriction, mitigates cybersickness by blacking out the peripheral region of the user’s FOV. However, this approach reduces the visibility of the virtual environment. We propose peripheral teleportation, a novel technique that creates a rest frame (RF) in the user's peripheral vision using content rendered from the current virtual environment. Specifically, the peripheral region is rendered by a pair of RF cameras whose transforms are updated by the user's physical motion. We apply alternating teleportations during translations, or snap turns during rotations, to the RF cameras to keep them close to the current viewpoint transformation. Consequently, the optical flow generated by RF cameras matches the user's physical motion, creating a stable peripheral view. In a between-subjects study (N=90), we compared peripheral teleportation with a traditional black FOV restrictor and an unrestricted control condition. The results showed that peripheral teleportation significantly reduced discomfort and enabled participants to stay immersed in the virtual environment for a longer duration of time. Overall, these findings suggest that peripheral teleportation is a promising technique that VR practitioners may consider adding to their cybersickness mitigation toolset.},
note = {Best Paper Award, IEEE VR 2025},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Mitigating cybersickness can improve the usability of virtual reality (VR) and increase its adoption. The most widely used technique, dynamic field-of-view (FOV) restriction, mitigates cybersickness by blacking out the peripheral region of the user’s FOV. However, this approach reduces the visibility of the virtual environment. We propose peripheral teleportation, a novel technique that creates a rest frame (RF) in the user's peripheral vision using content rendered from the current virtual environment. Specifically, the peripheral region is rendered by a pair of RF cameras whose transforms are updated by the user's physical motion. We apply alternating teleportations during translations, or snap turns during rotations, to the RF cameras to keep them close to the current viewpoint transformation. Consequently, the optical flow generated by RF cameras matches the user's physical motion, creating a stable peripheral view. In a between-subjects study (N=90), we compared peripheral teleportation with a traditional black FOV restrictor and an unrestricted control condition. The results showed that peripheral teleportation significantly reduced discomfort and enabled participants to stay immersed in the virtual environment for a longer duration of time. Overall, these findings suggest that peripheral teleportation is a promising technique that VR practitioners may consider adding to their cybersickness mitigation toolset. |
 | Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman; Kaori Hirano; Tabitha Peck; Alice Guth; Evan Suma Rosenberg; Tongyu Nie Reduction of Motion Complexity as an Objective Indicator of Cybersickness in Virtual Reality Proceedings Article In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR) 2025., pp. 1-9, 2025. @inproceedings{DeGuzman2025Reduction,
title = {Reduction of Motion Complexity as an Objective Indicator of Cybersickness in Virtual Reality},
author = {Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman and Kaori Hirano and Tabitha Peck and Alice Guth and Evan Suma Rosenberg and Tongyu Nie},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/2025_IEEE_VR_Motion_Complexity-1.pdf},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-02-25},
urldate = {2025-02-25},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Virtual Reality and 3D User Interfaces (IEEE VR) 2025.},
pages = {1-9},
abstract = {Subjective measures, such as the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ), Fast Motion Sickness Questionnaire (FMS), and discomfort scores, are widely used to assess cybersickness, but they often interrupt the user experience and are prone to bias. To overcome these limitations, researchers have also investigated objective indicators, though some approaches, such as using physiological data, can be cumbersome and impractical. Based on the loss of complexity hypothesis, which suggests that certain conditions, such as disease or aging, can produce a reduction of complexity in physiological system dynamics, we conducted an initial investigation of the relationship between movement complexity and cybersickness. We analyzed motion tracking collected from two previous cybersickness studies using the d95 score, a complexity metric derived using principal component analysis. The results revealed a systematic relationship between movement complexity and cybersickness across both experiments. Higher discomfort scores were associated with a reduction in complexity, thereby supporting the loss of complexity hypothesis. Furthermore, the 9-DOF complexity measure, which includes both physical head movement and virtual camera motion, was a more sensitive indicator than the 6-DOF measure computed from physical movements alone. These initial findings suggest that movement complexity may be a useful objective indicator for future cybersickness research.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Subjective measures, such as the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ), Fast Motion Sickness Questionnaire (FMS), and discomfort scores, are widely used to assess cybersickness, but they often interrupt the user experience and are prone to bias. To overcome these limitations, researchers have also investigated objective indicators, though some approaches, such as using physiological data, can be cumbersome and impractical. Based on the loss of complexity hypothesis, which suggests that certain conditions, such as disease or aging, can produce a reduction of complexity in physiological system dynamics, we conducted an initial investigation of the relationship between movement complexity and cybersickness. We analyzed motion tracking collected from two previous cybersickness studies using the d95 score, a complexity metric derived using principal component analysis. The results revealed a systematic relationship between movement complexity and cybersickness across both experiments. Higher discomfort scores were associated with a reduction in complexity, thereby supporting the loss of complexity hypothesis. Furthermore, the 9-DOF complexity measure, which includes both physical head movement and virtual camera motion, was a more sensitive indicator than the 6-DOF measure computed from physical movements alone. These initial findings suggest that movement complexity may be a useful objective indicator for future cybersickness research. |
2024
|
 | Zubin Choudhary; Laura Battistel; Raiffa Syamil; Hiroshi Furuya; Ferran Argelaguet; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F. Welch Examining the Effects of Teleportation on Semantic Memory of a Virtual Museum Compared to Natural Walking Proceedings Article In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence and Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (ICAT-EGVE 2024), Tsukuba, Japan, December 1-3, 2024, pp. 1-12, 2024. @inproceedings{Choudhary2024walking,
title = {Examining the Effects of Teleportation on Semantic Memory of a Virtual Museum Compared to Natural Walking},
author = {Zubin Choudhary and Laura Battistel and Raiffa Syamil and Hiroshi Furuya and Ferran Argelaguet and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F. Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/paper1028_2.pdf},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-12-01},
urldate = {2024-12-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence and Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (ICAT-EGVE 2024), Tsukuba, Japan, December 1-3, 2024},
pages = {1-12},
abstract = {Over the past decades there has been extensive research investigating the trade-offs between various Virtual Reality (VR) locomotion techniques. One of the most highly researched techniques is teleportation, due to its ability to quickly traverse large virtual spaces even in limited physical tracking spaces. The majority of teleportation research has been focused on its effects on spatial cognition, such as spatial understanding and retention. However, relatively little is known about whether the use of teleportation in immersive learning experiences can effect the acquisition of semantic knowledge — our knowledge about facts, concepts, and ideas — which is essential for long-term learning. In this paper we present a human-subjects study to investigate the effects of teleportation compared to natural walking on the retention of semantic information about artifacts in a virtual museum. Participants visited unique 3D artifacts accompanied by audio clips and artifact names. Our results show that participants reached the same semantic memory performance with both locomotion techniques but with different behaviors, self-assessed performance, and preference. In particular, participants subjectively indicated that they felt that they recalled more semantic memory with walking than teleportation. However, objectively, they spent more time with the artifacts while walking, meaning that they learnt less per a set amount of time than with teleportation. We discuss the relationships, implications, and guidelines for VR experiences designed to help users acquire new knowledge.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Over the past decades there has been extensive research investigating the trade-offs between various Virtual Reality (VR) locomotion techniques. One of the most highly researched techniques is teleportation, due to its ability to quickly traverse large virtual spaces even in limited physical tracking spaces. The majority of teleportation research has been focused on its effects on spatial cognition, such as spatial understanding and retention. However, relatively little is known about whether the use of teleportation in immersive learning experiences can effect the acquisition of semantic knowledge — our knowledge about facts, concepts, and ideas — which is essential for long-term learning. In this paper we present a human-subjects study to investigate the effects of teleportation compared to natural walking on the retention of semantic information about artifacts in a virtual museum. Participants visited unique 3D artifacts accompanied by audio clips and artifact names. Our results show that participants reached the same semantic memory performance with both locomotion techniques but with different behaviors, self-assessed performance, and preference. In particular, participants subjectively indicated that they felt that they recalled more semantic memory with walking than teleportation. However, objectively, they spent more time with the artifacts while walking, meaning that they learnt less per a set amount of time than with teleportation. We discuss the relationships, implications, and guidelines for VR experiences designed to help users acquire new knowledge. |
 | Hiroshi Furuya; Zubin Choudhary; Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman; Matt Gottsacker; Gerd Bruder; Greg Welch Using Simulated Real-world Terrain in VR to Study Outdoor AR Topographic Map Interfaces Proceedings Article In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence and Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (ICAT-EGVE 2024), Tsukuba, Japan, December 1-3, 2024, pp. 1-10, 2024. @inproceedings{Furuya2024topo,
title = {Using Simulated Real-world Terrain in VR to Study Outdoor AR Topographic Map Interfaces},
author = {Hiroshi Furuya and Zubin Choudhary and Jasmine Joyce DeGuzman and Matt Gottsacker and Gerd Bruder and Greg Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/cameraready_ICAT_EGVE_2024_1029_topographic_map.pdf},
doi = {tbd},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-12-01},
urldate = {2024-12-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence and Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (ICAT-EGVE 2024), Tsukuba, Japan, December 1-3, 2024},
pages = {1-10},
abstract = {Augmented reality (AR) technology enables advanced integration of spatial information useful in a variety of important domains, including for reading topographic maps in the field. It is also important to understand how this technology may potentially affect spatial learning ability. In this paper, we demonstrate the use of virtual reality (VR) to conduct a human-subject study investigating the impacts of different simulated AR topographic map interface designs on spatial learning outcomes. Our results show that interfaces that encourage engagement with the interface instead of with the map and the environment result in fast task completion times but poor spatial learning. We also found participant preference for a novel interface design that assists users with map orientation without explicitly guiding the user through the task.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Augmented reality (AR) technology enables advanced integration of spatial information useful in a variety of important domains, including for reading topographic maps in the field. It is also important to understand how this technology may potentially affect spatial learning ability. In this paper, we demonstrate the use of virtual reality (VR) to conduct a human-subject study investigating the impacts of different simulated AR topographic map interface designs on spatial learning outcomes. Our results show that interfaces that encourage engagement with the interface instead of with the map and the environment result in fast task completion times but poor spatial learning. We also found participant preference for a novel interface design that assists users with map orientation without explicitly guiding the user through the task. |
 | Matt Gottsacker; Hiroshi Furuya; Laura Battistel; Carlos Pinto Jimenez; Nicholas LaMontagna; Gerd Bruder; and Gregory F. Welch Exploring Spatial Cognitive Residue and Methods to Clear Users’ Minds When Transitioning Between Virtual Environments Proceedings Article In: IEEE International Symposium of Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), pp. 1-11, 2024. @inproceedings{nokey,
title = {Exploring Spatial Cognitive Residue and Methods to Clear Users’ Minds When Transitioning Between Virtual Environments},
author = {Matt Gottsacker and Hiroshi Furuya and Laura Battistel and Carlos Pinto Jimenez and Nicholas LaMontagna and Gerd Bruder and and Gregory F. Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/ISMAR24____Conference____Residue-5.pdf},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-21},
urldate = {2024-10-21},
booktitle = {IEEE International Symposium of Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR)},
pages = {1-11},
abstract = {In most cases, retaining memories of things we have experienced in the past is desirable, but in some cases, we want to clear our minds so that we may focus completely on subsequent activities. When someone switches from one task to another, they commonly incur some “cognitive residue” where some of their cognitive resources such as working memory and attention remain devoted to their previous task even after they try to switch their focus to their new task. This residue could have a negative impact on their performance in the next task, and in such circumstances, it is important to reduce that residue. In this paper, we explore the concept of cognitive residue in the context of switching between virtual reality (VR) environments. We conducted a human-subject experiment (N=24) with a spatial recall task to investigate how different visual transitions might reduce participants’ spatial cognitive residue. In this instance, more errors on the recall task corresponds to less spatial cognitive residue. We found that transitions that lasted one minute successfully reduced spatial cognitive residue: they significantly reduced participants’ abilities to recall the positions of objects in their previous VE compared to an instantaneous cut transition. Additionally, for transitions that showed a nature scene, greater head movement significantly correlated with more spatial memory errors (i.e., less spatial cognitive residue). We discuss how these findings can be applied to support users transitioning between virtual tasks and environments in VR task switching scenarios.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
In most cases, retaining memories of things we have experienced in the past is desirable, but in some cases, we want to clear our minds so that we may focus completely on subsequent activities. When someone switches from one task to another, they commonly incur some “cognitive residue” where some of their cognitive resources such as working memory and attention remain devoted to their previous task even after they try to switch their focus to their new task. This residue could have a negative impact on their performance in the next task, and in such circumstances, it is important to reduce that residue. In this paper, we explore the concept of cognitive residue in the context of switching between virtual reality (VR) environments. We conducted a human-subject experiment (N=24) with a spatial recall task to investigate how different visual transitions might reduce participants’ spatial cognitive residue. In this instance, more errors on the recall task corresponds to less spatial cognitive residue. We found that transitions that lasted one minute successfully reduced spatial cognitive residue: they significantly reduced participants’ abilities to recall the positions of objects in their previous VE compared to an instantaneous cut transition. Additionally, for transitions that showed a nature scene, greater head movement significantly correlated with more spatial memory errors (i.e., less spatial cognitive residue). We discuss how these findings can be applied to support users transitioning between virtual tasks and environments in VR task switching scenarios. |
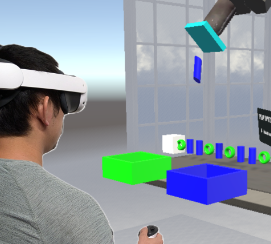 | Hiroshi Furuya; Laura Battistel; Zubin Datta Choudhary; Matt Gottsacker; Gerd Bruder; Gregory F Welch Difficulties in Perceiving and Understanding Robot Reliability Changes in a Sequential Binary Task Proceedings Article In: Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Symposium on Spatial User Interaction, pp. 1-11, Association for Computing Machinery, Trier, Germany, 2024, ISBN: 9798400710889. @inproceedings{Furuya2024perceive,
title = {Difficulties in Perceiving and Understanding Robot Reliability Changes in a Sequential Binary Task},
author = {Hiroshi Furuya and Laura Battistel and Zubin Datta Choudhary and Matt Gottsacker and Gerd Bruder and Gregory F Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/SUI_2024___Difficulties_in_Perceiving_and_Understanding_Robot_Reliability_Changes_in_a_Sequential_Binary_Task-1-2.pdf},
doi = {10.1145/3677386.3682083},
isbn = {9798400710889},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-10-07},
urldate = {2024-10-07},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2024 ACM Symposium on Spatial User Interaction},
pages = {1-11},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {Trier, Germany},
series = {SUI '24},
abstract = {Human-robot teams push the boundaries of what both humans and robots can accomplish. In order for the team to function well, the human must accurately assess the robot’s capabilities to calibrate the trust between the human and robot. In this paper, we use virtual reality (VR), a widely accepted tool in studying human-robot interaction (HRI), to study human behaviors affecting their detection and understanding of changes in a simulated robot’s reliability. We present a human-subject study to see how different reliability change factors may affect this process. Our results demonstrate that participants make judgements about robot reliability before they have accumulated sufficient evidence to make objectively high-confidence inferences about robot reliability. We show that this reliability change observation behavior diverges from behavior expectations based on the probability distribution functions used to describe observation outcomes.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Human-robot teams push the boundaries of what both humans and robots can accomplish. In order for the team to function well, the human must accurately assess the robot’s capabilities to calibrate the trust between the human and robot. In this paper, we use virtual reality (VR), a widely accepted tool in studying human-robot interaction (HRI), to study human behaviors affecting their detection and understanding of changes in a simulated robot’s reliability. We present a human-subject study to see how different reliability change factors may affect this process. Our results demonstrate that participants make judgements about robot reliability before they have accumulated sufficient evidence to make objectively high-confidence inferences about robot reliability. We show that this reliability change observation behavior diverges from behavior expectations based on the probability distribution functions used to describe observation outcomes. |
 | Matt Gottsacker; Hiroshi Furuya; Zubin Choudhary; Austin Erickson; Ryan Schubert; Gerd Bruder; Michael P. Browne; Gregory F. Welch Investigating the relationships between user behaviors and tracking factors on task performance and trust in augmented reality Journal Article In: Elsevier Computers & Graphics, vol. 123, pp. 1-14, 2024. @article{gottsacker2024trust,
title = {Investigating the relationships between user behaviors and tracking factors on task performance and trust in augmented reality},
author = {Matt Gottsacker and Hiroshi Furuya and Zubin Choudhary and Austin Erickson and Ryan Schubert and Gerd Bruder and Michael P. Browne and Gregory F. Welch},
url = {https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/C_G____ARTrust____Accuracy___Precision.pdf},
doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cag.2024.104035},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-08-06},
urldate = {2024-08-06},
journal = {Elsevier Computers & Graphics},
volume = {123},
pages = {1-14},
abstract = {This research paper explores the impact of augmented reality (AR) tracking characteristics, specifically an AR head-worn display's tracking registration accuracy and precision, on users' spatial abilities and subjective perceptions of trust in and reliance on the technology. Our study aims to clarify the relationships between user performance and the different behaviors users may employ based on varying degrees of trust in and reliance on AR. Our controlled experimental setup used a 360 field-of-regard search-and-selection task and combines the immersive aspects of a CAVE-like environment with AR overlays viewed with a head-worn display. We investigated three levels of simulated AR tracking errors in terms of both accuracy and precision (+0, +1, +2). We controlled for four user task behaviors that correspond to different levels of trust in and reliance on an AR system: AR-Only (only relying on AR), AR-First (prioritizing AR over real world), Real-Only (only relying on real world), and Real-First (prioritizing real world over AR). By controlling for these behaviors, our results showed that even small amounts of AR tracking errors had noticeable effects on users' task performance, especially if they relied completely on the AR cues (AR-Only). Our results link AR tracking characteristics with user behavior, highlighting the importance of understanding these elements to improve AR technology and user satisfaction.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
This research paper explores the impact of augmented reality (AR) tracking characteristics, specifically an AR head-worn display's tracking registration accuracy and precision, on users' spatial abilities and subjective perceptions of trust in and reliance on the technology. Our study aims to clarify the relationships between user performance and the different behaviors users may employ based on varying degrees of trust in and reliance on AR. Our controlled experimental setup used a 360 field-of-regard search-and-selection task and combines the immersive aspects of a CAVE-like environment with AR overlays viewed with a head-worn display. We investigated three levels of simulated AR tracking errors in terms of both accuracy and precision (+0, +1, +2). We controlled for four user task behaviors that correspond to different levels of trust in and reliance on an AR system: AR-Only (only relying on AR), AR-First (prioritizing AR over real world), Real-Only (only relying on real world), and Real-First (prioritizing real world over AR). By controlling for these behaviors, our results showed that even small amounts of AR tracking errors had noticeable effects on users' task performance, especially if they relied completely on the AR cues (AR-Only). Our results link AR tracking characteristics with user behavior, highlighting the importance of understanding these elements to improve AR technology and user satisfaction. |
 | Gerd Bruder; Michael Browne; Zubin Choudhary; Austin Erickson; Hiroshi Furuya; Matt Gottsacker; Ryan Schubert; Gregory Welch Visual Factors Influencing Trust and Reliance with Augmented Reality Systems Journal Article In: Journal of Vision Abstracts—Vision Sciences Society (VSS) Annual Meeting, 2024. @article{Bruder2024,
title = {Visual Factors Influencing Trust and Reliance with Augmented Reality Systems},
author = {Gerd Bruder and Michael Browne and Zubin Choudhary and Austin Erickson and Hiroshi Furuya and Matt Gottsacker and Ryan Schubert and Gregory Welch},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-05-17},
urldate = {2024-05-17},
journal = {Journal of Vision Abstracts—Vision Sciences Society (VSS) Annual Meeting},
abstract = {Augmented Reality (AR) systems are increasingly used for simulations, training, and operations across a wide range of application fields. Unfortunately, the imagery that current AR systems create often does not match our visual perception of the real world, which can make users feel like the AR system is not believable. This lack of belief can lead to negative training or experiences, where users lose trust in the AR system and adjust their reliance on AR. The latter is characterized by users adopting different cognitive perception-action pathways by which they integrate AR visual information for spatial tasks. In this work, we present a series of six within-subjects experiments (each N=20) in which we investigated trust in AR with respect to two display factors (field of view and visual contrast), two tracking factors (accuracy and precision), and two network factors (latency and dropouts). Participants performed a 360-degree visual search-and-selection task in a hybrid setup involving an AR head-mounted display and a CAVE-like simulated real environment. Participants completed the experiments with four perception-action pathways that represent different levels of the users’ reliance on an AR system: AR-Only (only relying on AR), AR-First (prioritizing AR over real world), Real-First (prioritizing real world over AR), and Real-Only (only relying on real world). Our results show that participants’ perception-action pathways and objective task performance were significantly affected by all six tested AR factors. In contrast, we found that their subjective responses for trust and reliance were often more affected by slight AR system differences than would elicit objective performance differences, and participants tended to overestimate or underestimate the trustworthiness of the AR system. Participants showed significantly higher task performance gains if their sense of trust was well-calibrated to the trustworthiness of the AR system, highlighting the importance of effectively managing users’ trust in future AR systems.
Acknowledgements: This material includes work supported in part by Vision Products LLC via US Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) Award Number FA864922P1038, and the Office of Naval Research under Award Numbers N00014-21-1-2578 and N00014-21-1-2882 (Dr. Peter Squire, Code 34).},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Augmented Reality (AR) systems are increasingly used for simulations, training, and operations across a wide range of application fields. Unfortunately, the imagery that current AR systems create often does not match our visual perception of the real world, which can make users feel like the AR system is not believable. This lack of belief can lead to negative training or experiences, where users lose trust in the AR system and adjust their reliance on AR. The latter is characterized by users adopting different cognitive perception-action pathways by which they integrate AR visual information for spatial tasks. In this work, we present a series of six within-subjects experiments (each N=20) in which we investigated trust in AR with respect to two display factors (field of view and visual contrast), two tracking factors (accuracy and precision), and two network factors (latency and dropouts). Participants performed a 360-degree visual search-and-selection task in a hybrid setup involving an AR head-mounted display and a CAVE-like simulated real environment. Participants completed the experiments with four perception-action pathways that represent different levels of the users’ reliance on an AR system: AR-Only (only relying on AR), AR-First (prioritizing AR over real world), Real-First (prioritizing real world over AR), and Real-Only (only relying on real world). Our results show that participants’ perception-action pathways and objective task performance were significantly affected by all six tested AR factors. In contrast, we found that their subjective responses for trust and reliance were often more affected by slight AR system differences than would elicit objective performance differences, and participants tended to overestimate or underestimate the trustworthiness of the AR system. Participants showed significantly higher task performance gains if their sense of trust was well-calibrated to the trustworthiness of the AR system, highlighting the importance of effectively managing users’ trust in future AR systems.
Acknowledgements: This material includes work supported in part by Vision Products LLC via US Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) Award Number FA864922P1038, and the Office of Naval Research under Award Numbers N00014-21-1-2578 and N00014-21-1-2882 (Dr. Peter Squire, Code 34). |



![[Poster] Can You See It? Evaluating Color Visibility in Simulated Outdoor Environments](https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/teaser_AA-150x150.png)







![[Poster] Inducing Unintentional Positional Drift (UPD) in Virtual Reality via Physical Rotations and the Illusion of Leaning](https://sreal.ucf.edu/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/Roll-Example-e1741105590923-150x150.jpg)









